Now, if we take our root position C major triad in close voicing and raise the lowest note in the structure up one octave we get a major triad in first inversion That is, the 3rd of the chord is now in the bass In figured bass notation, this is called a sixthree voicing If we apply this process to the sixthree voicing we get a second inversion major triad That is, the 5th of the chord isFor example, if, in an augmented G sharp major chord, you rewrite the D double sharp as an E natural, the triad becomes an E augmented chord Figure 518 Changing the spelling of any note in a chord also changes the chord's name You can put the chord in a different position or add more of the samenamed notes at other octaves without changing the name of the chord ButHost a game Live Game Live Homework Solo Practice Practice Play Share practice link Finish Editing This quiz is incomplete!
Triads And Seventh Chords Open Music Theory
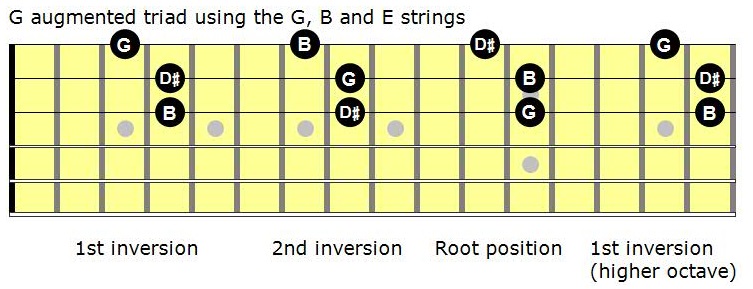
G augmented triad in root position
G augmented triad in root position-Triads in Root Position Edited DRAFT a year ago by juanrodriguez Played 11 times 0 University Arts 86% average accuracy 0 Save Edit Edit Print;Last time I you showed a new triad type, augmented, and various ways of transforming a C chord to C augmented This time I'll do the same thing, but with G major and G augmented The Work Remember that a major triad is made of three notes, the root, the third, and the fifth, and an augmented triad is the same, but with the fifth augmented, or raised by a half step Example 1




A Complete Guide To Chord Symbols In Music Musicnotes Now
Blog Latest News g major triad / 0 Comments / in Uncategorized / by / 0 Comments / in Uncategorized / byGflat augmented triad chord The Solution below shows the Gflat augmented triad chord in root position, 1st inversion and 2nd inversion on the piano, treble clef and bass clef The Lesson steps then explain how to construct this triad chord using the 3rd and 5th note intervals, then finally how to construct the inverted chord variations For a quick summary of this topic, have a look atIn music theory, this triad chord as it stands is said to be in root position because the root of the chord note G, is the note with the lowest pitch of all the triad notes The chord spelling / formula relative to the G major scale is 1 3 #5 G, G aug, G Augmented Notes G, B, D♯ Additionally, you can Download our Piano Companion FREE app which is used by millions of users worldwide and
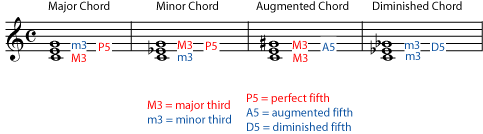
In this case, the chord is viewed as a C major seventh chord (CM 7) in which the third note is an augmented fifth from root (G ♯), rather than a perfect fifth from root (G) All chord names and symbols including altered fifths, ie, augmented (♯ 5, 5, aug5) or diminished (♭ 5, o 5, dim5) fifths can be interpreted in a similar way Common types of chords Triads The four triads, all Here you see a G Major and G Minor triad We build these off of the G Major scale So, in this case, G is considered the "root" of the chord Then we take the 3rd and 5th notes of the G major scale, which are B and D This gives you the major triad!The augmented triad has a major third on both the bottom and top Major Minor Diminished Augmented Unable to play MP3 Unable to play MP3 Unable to play MP3 Unable to play MP3 Triad Inversions Triads can appear in three inversions The inversion is determined by the lowest note of the chord In root position the root is the the lowest note In first inversion the third is the the
A note that is diatonic to the key of C minor Because of this fact the D# is often written as a Eb Root position Close Voicing/Open Voicing Augmented Diminished Triad• The augmented triad is the same shape in all 3 inversions, but it is arrived at by changing a different note on each string • Go through the circle of 5ths starting with root position AThere are three halfsteps in between, so the major third is the note that is four halfsteps above the root An augmented triad is built by stacking two of these on top of each other For C major I would needMajor Triads Hopefully you've read about major scales already;




Augmented Triads The Nandi Method




C5s1 Chords
For example, if, in an augmented G major chord, you rewrite the D double sharp as an E natural, the triad becomes an E augmented chord You can put the chord in a different position or add more of the samenamed notes at other octaves without changing the name of the chord But changing the note names or adding differentnamed notes, will change the name of theG Augmented triads A;C augmented triad chord The Solution below shows the C augmented triad chord in root position, 1st inversion and 2nd inversion on the piano, treble clef and bass clef The Lesson steps then explain how to construct this triad chord using the 3rd and 5th note intervals, then finally how to construct the inverted chord variations For a quick summary of this topic, have a look at Triad



Augmented And Diminished Chords Open Textbooks For Hong Kong



Naming Major Or Minor Triads In Music Theory Chord Inversions
Root Position Root position triads have the lowest note as the root of the chord Root on 654 play notes play chord Root on 543 play notes play chord Root on 432 play notes play chord Root on 321 play notes play chord First Inversion First inversion triads have the highest note as the root of the chord 1st Inversion onThe augmented sixth is generally used as a dissonant interval most commonly used in motion towards a dominant chord in root position (with the root doubled to create the octave the augmented sixth chord resolves to) or to a tonic chord in second inversion (a tonic triad with the fifth doubled for the same purpose) In this case, the tonic note of the key is included in the For example, if, in an augmented G sharp major chord, you rewrite the D double sharp as an E natural, the triad becomes an E augmented chord Figure \(\PageIndex{14}\) Changing the spelling of any note in a chord also changes the chord's name You can put the chord in a different position or add more of the samenamed notes at other octaves without changing the



13 Triads Fundamentals Function And Form




Augmented Sixth Chord Wikipedia
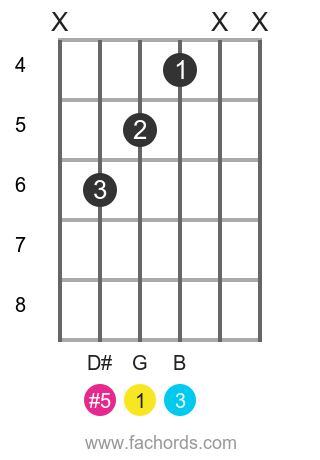
Triads in Root Position 4 months ago by Jill Brooks 78% average accuracy 28 plays 9th 12th grade Arts 1 Save Share Copy and Edit Edit Super resource With Super, get unlimited access to this resource and over 100,000 other Super resources Thank you for being Super Get unlimited access to this and over 100,000 Super resources Get Super This quiz is incomplete!A triad is in root position when the root is the lowest chord tone (in the bass) In this position, the third and fifth are vertically stacked "on top" of the root Figured bass notation identifies this as 5/3 Because of its close correlation with the overtone series, the root position is the most stable position of a major or minor triad Below are triads in root position (or 5/3 positionAll information about Guitar Triad G Augmented, Root Position Notes GBD# Formula 1,3,#5 Free guitar triads for beginner or advanced guitarists




Click Here To A Pdf Of The Lesson




13 Ear Training Basic Triads Music Student 101
Triads are named according to their root and quality The triad in Example 13–6a, for example, is a Gmajor triad and the triad in Example 13–6b is a Gminor triad Triads may be built on any note The following example shows an EA diminished triad's third is minor and its fifth is diminished, while an augmented triad's third is major and its fifth is augmented In chordsymbol notation, major triads are represented with capital letters that correspond to the triad's root Minor triads have a lowercase "m" after the letter, diminished triads have a lowercase "dim" or a degre e sign ("°"), and augmentedThe figured bass notation for a triad in root position is 5/3, with the 5 placed above the 3 on a staff diagram These numbers represent the interval between the lowest note of the chord and the note in question So another name for this chord would be G major triad in fivethree position



Basicmusictheory Com A Flat Augmented Triad Chord




A Complete Guide To Chord Symbols In Music Musicnotes Now
The Augmented triad rooted on the fifth note of a Minor key is also frequently used It should be noted that the D# in the Augmented triad is enharmonic to Eb; When the triad is in its Root3rd5th configuration we call it 'root position' – C,E,G If we move the root up an octave we have the first inversion – 3rd, 5th, Root – E,G,C If we then move the 3rd up an octave we have the second inversion – 5th, Root, 3rd – G,C,E OTHER TRIADS It is really simple to find other (minor, augmented, diminished) triads from the major triad MajorTo play this quiz, please finish editing it Delete Quiz This quiz is incomplete




5 2 Naming Triads



1
When in root position (the root note is on the bottom) each note is a third away from the last (if intervals are new to you check out the intervals tutorial) Triads are a basic chord structure and the basis of how other types of chords are constructed There are four types of triads Major;Skip to content GLI Network MenuDiminished triads root (1), minor 3rd (b3) and diminished 5th (b5) 1 b3 b5 Augmented triads root (1), major 3rd (3) and augmented 5th (#5) 1 3 #5 Note In the video, we didn't use augmented triads, because they don't exist in the particular scale we were harmonizing That doesn't mean you can't try using them in places Your ears are




Rob Silver Four String Augmented Triad Arpeggios For 8 String Guitar All String And All Inversions



Gaug Guitar Chord Guitar Chords Chart
An indepth review of harmonic and melodic root position diminished triads Includes notereading drills for all triadsFree PDF File http//pianopowercom/Then you simply flat the 3rd (lower one halfstep) to make it a minor triadAugmented triad M3 and A5 above the root (as in me–sol–ti) Leadsheet symbols A triad can be summed up by a single symbol, such as a leadsheet chord symbol A lead sheet symbol includes information about both root quality, as well as which pitch class occurs in the lowest voice (called the bass regardless of who is singing or playing that pitch) A leadsheet symbol begins with a



B Flat Augmented Chord Chord Walls




Learn 5 Ways To Play A Augmented Chord By Chord Acoustic Guitar
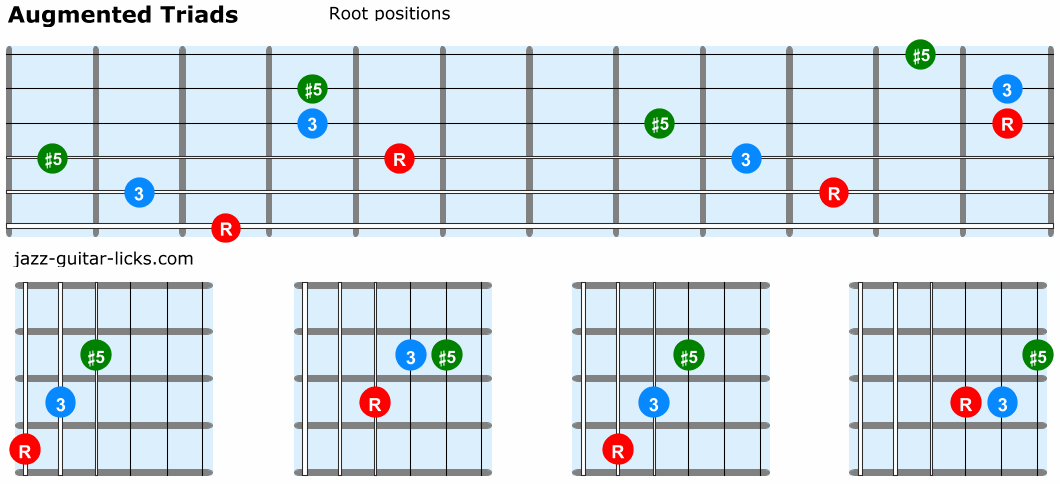
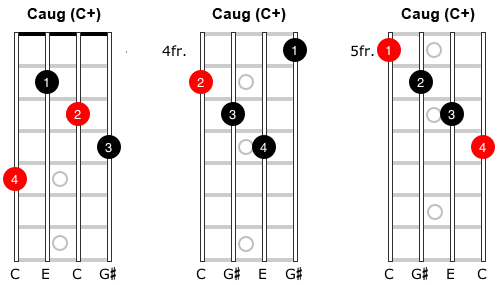
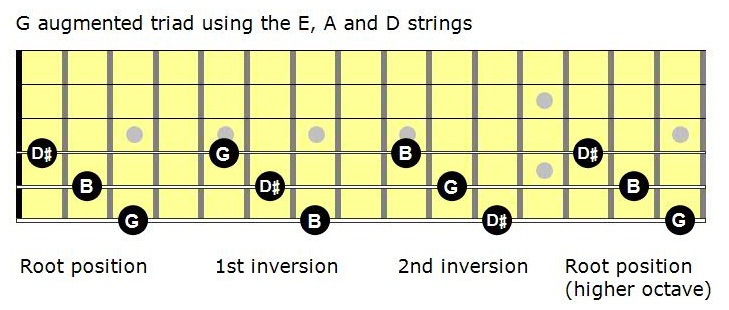
The figured bass notation for a triad in root position is 5/3, with the 5 placed above the 3 on a staff diagram These numbers represent the interval between the lowest note of the chord and the note in question So another name for this chord would be G augmented triad in fivethree positionSo here's the F augmented root position arpeggio I just want to point out that the last root, F, can be moved to the B string if you want to make it a little easier Okay, here's the A augmented arpeggio, or the first "inversion" of the F augmented arpeggio, if you will And here's the G# augmented arpeggio Great, so practice these arpeggios The formula for an augmented triad Formula Root3rd#5 We are going to use the key of G for our examples, so using this formula, the notes in a G augmented triad would be GBD# Let's take a look at what an augmented triad looks like notated in root position, 1st inversion and 2nd inversion



Triads And Seventh Chords Open Music Theory




5 2 Naming Triads
Play each augmented triad in root position, then 1st inversion, then 2nd inversion Play each chord up and down the keyboard for at least 2 octaves maybe 3 octaves Play them with your left hand, then play them with your right hand Then play them hands together Go through all 12 major chords, inverting every one Then go through all the 12 minor chords,The figured bass notation for a triad in root position is 5/3, with the 5 placed above the 3 on a staff diagram These numbers represent the interval between the lowest note of the chord and the note in question So another name for this chord would be Gsharp augmented triadA Augmented triad root position (A) C# E# A Augmented triad 1st Inversion C# E# (A) A Augmented triad 2nd Inversion E# (A) C# B Augmented Triad Root Position (B) D# Fx B Augmented Triad 1st Inversion D# Fx (B) B Augmented Triad 2nd Version Fx (B) D# Sets found in the same folder Music Theory > Chords > Triads > Diminished 22 terms



The Piano Augmented Chord



Solved Write The Following Triads In Root Position Amp Inversion Write A Bass Clef On The Staff Course Hero
Start studying Augmented triad in (root position) Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools



Triads And Seventh Chords Open Music Theory



Triads And Seventh Chords Open Music Theory




G Sharp Augmented Chord On The Guitar G Diagrams Finger Positions Theory



Triad Chords 84 Guitar Shapes Lesson With Pdf



Northernoaks Greatheartsamerica Org Wp Content Uploads Sites 3 04 10 Choir Week Of 4 6 Pdf




Basicmusictheory Com A Augmented Triad Chord




Rob Silver Left Handed Augmented Triad Arpeggios 2 3 4 5 And 6 String Options In All Inversions And On All Strings
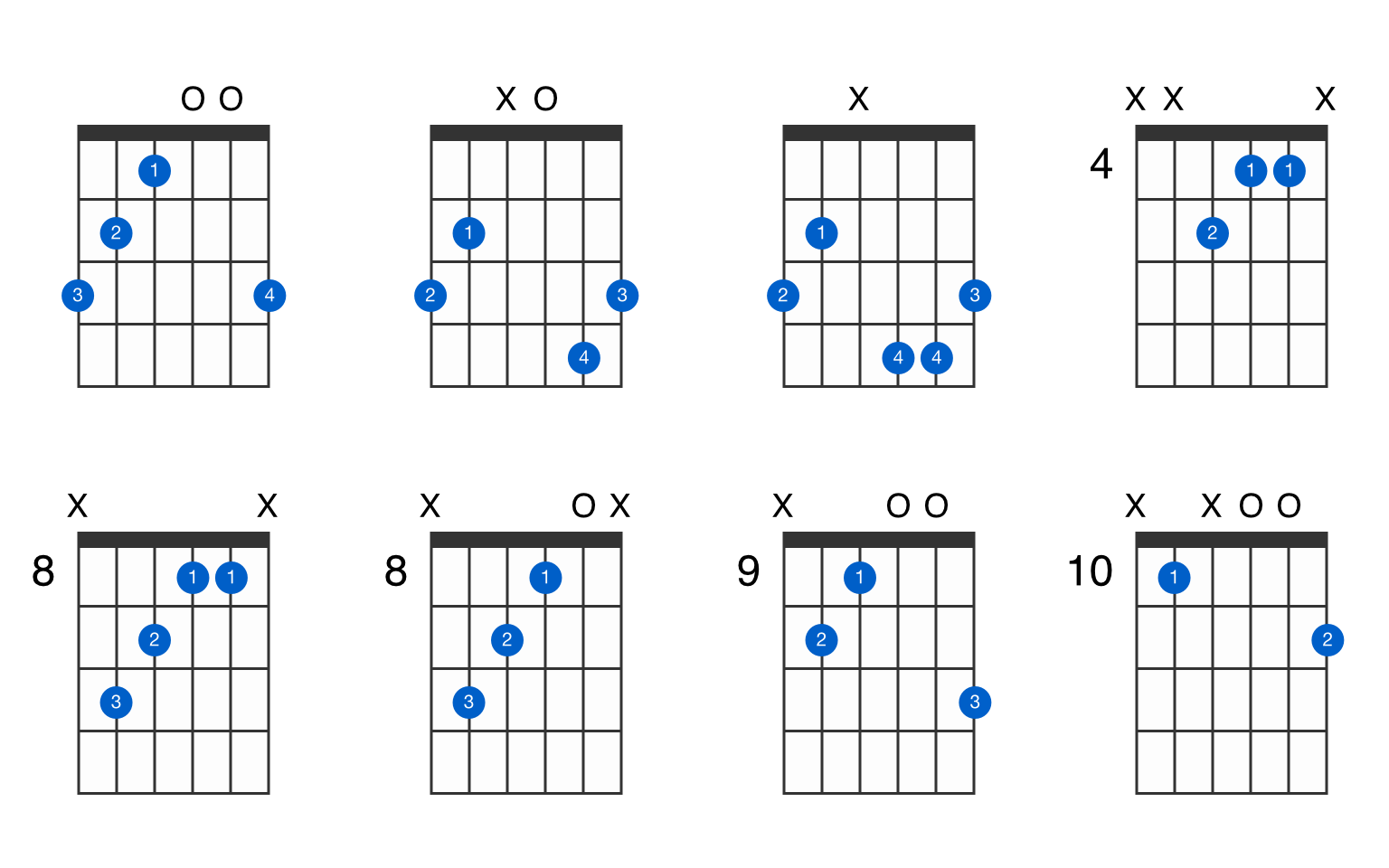



G Augmented Guitar Chord Gtrlib Chords
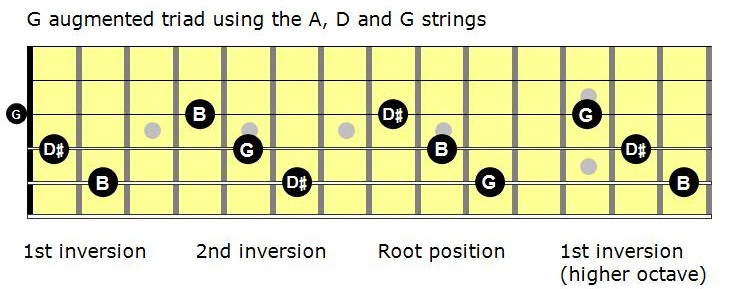



Mastering The Fretboard Augmented Triads Learn Jazz Standards




6 Ways To Play G Augmented Chord By Chord Acoustic Guitar




Basicmusictheory Com G Augmented Triad Chord




Major Triads Inversions Mrs Strauss S Music Theory Classes




Basicmusictheory Com G Flat Augmented Triad Chord
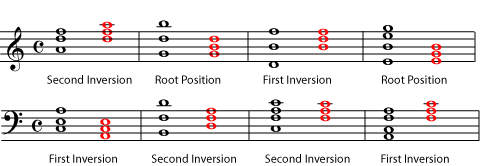



Music Triads Root Position Chord Inversions
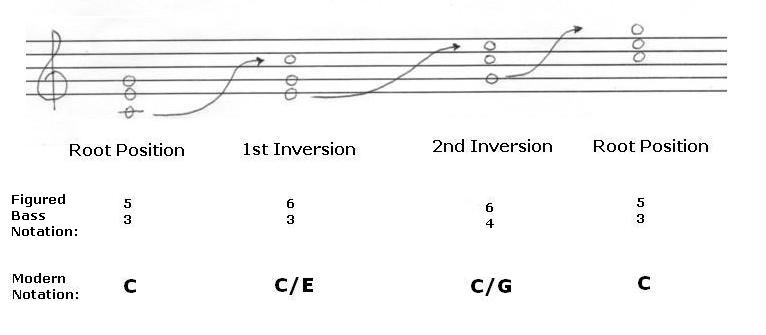



Lesson 12 Triads Part 1




Basicmusictheory Com G Augmented Triad Chord



Basicmusictheory Com A Flat Augmented Triad Chord




Basicmusictheory Com G Augmented Triad Chord



Http Learnmusictheory Net Pdfs Pdffiles 01 04 01 Introducingtriads Pdf




Triad Jens Larsen
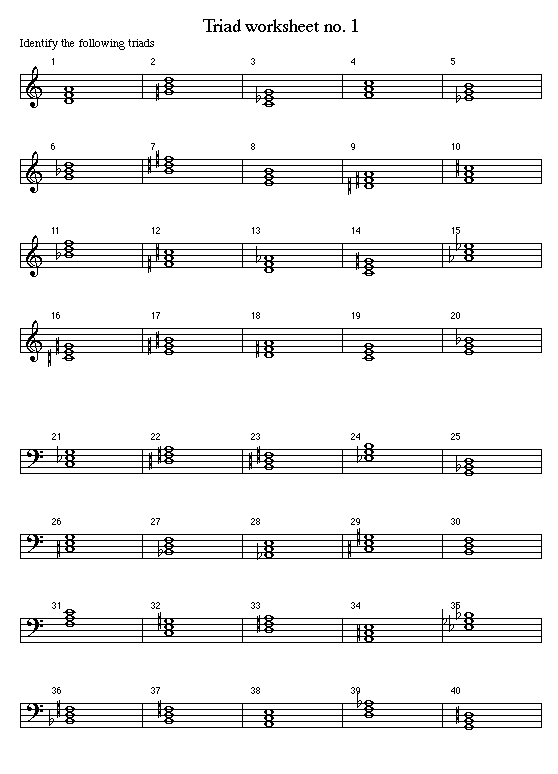



Triads



Part 1 Of Triads Inside Out Learning Your Closed Voicing Triad Inversions Ry Naylor Guitar



How To Play Triads On Guitar Jamieholroydguitar Com Jamie Holroyd Guitar




Basicmusictheory Com C Augmented Triad Chord




Augmented Guitar Chords Everything You Need To Know




Basicmusictheory Com G Augmented Triad Chord
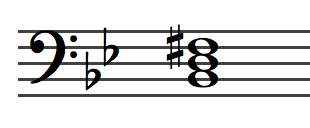



Triads Tonic Dominant Areas Kaitlin Bove Music




What Is An Inversion What Is The Difference With Root Position




6 Ways To Play G Augmented Chord By Chord Youtube
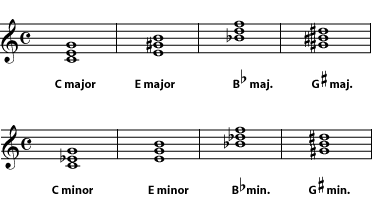



7 2 Naming Triads Humanities Libretexts




13 Ear Training Basic Triads Music Student 101
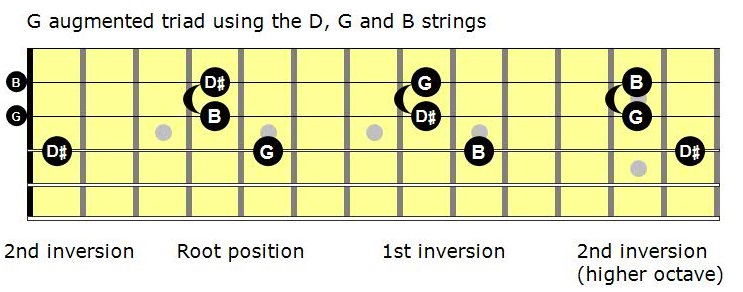



Mastering The Fretboard Augmented Triads Learn Jazz Standards




Basicmusictheory Com G Augmented Triad Chord
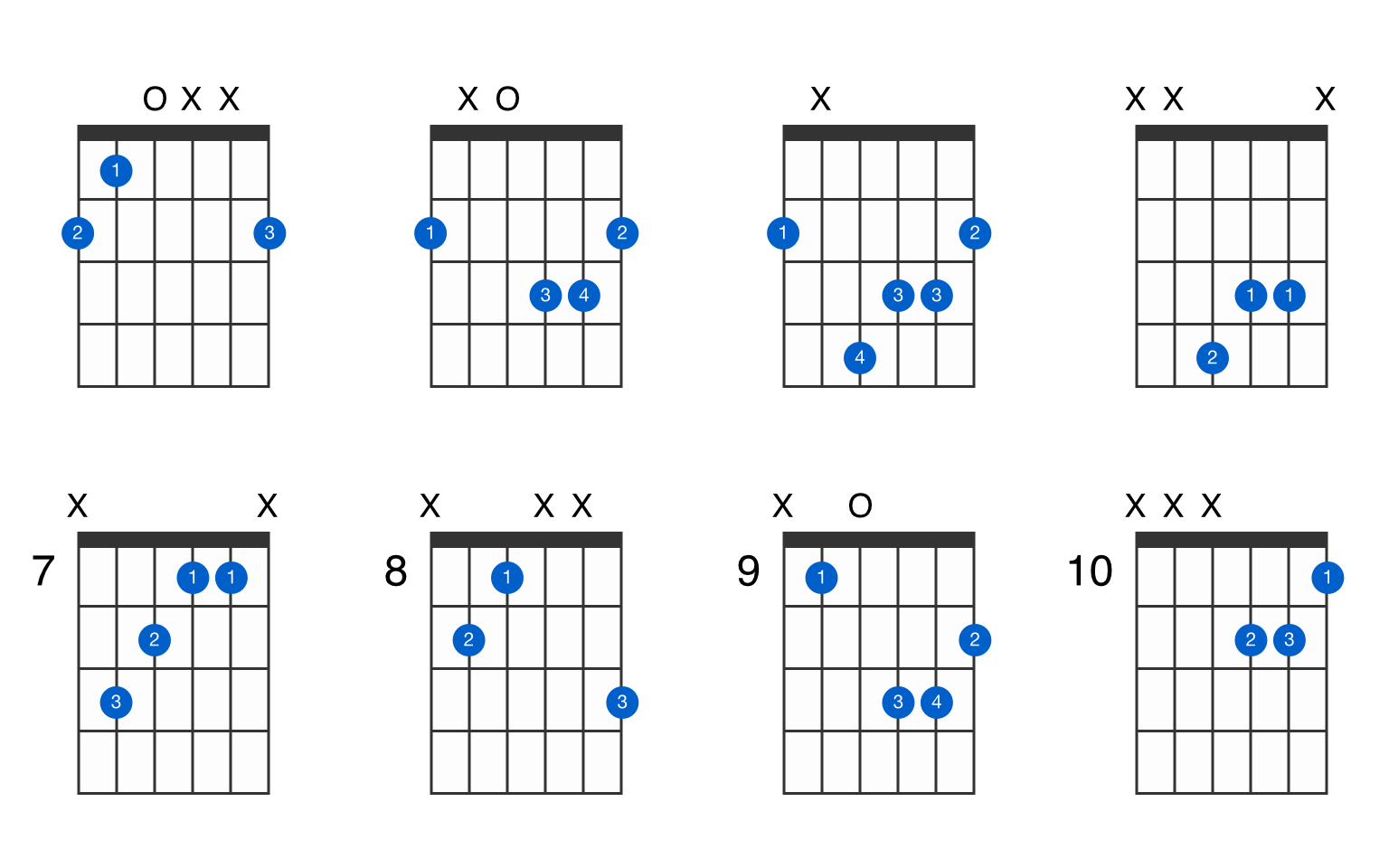



G Flat Augmented Guitar Chord Gtrlib Chords



The Augmented Chord Music Theory For Mandolin Simplymandolin



3



Triads And Seventh Chords Open Music Theory




Inverted Triads



When We Learn Open Position Guitar
/Triad_c_augmented.svg-583dbcb53df78c6f6a1f986e.png)



What Are Diminished And Augmented Triads



13 Triads Fundamentals Function And Form




Basicmusictheory Com G Sharp Augmented Triad Chord



Modern Music School



Mastering The Fretboard Augmented Triads Learn Jazz Standards




15 Triads And Scales



The Jazz Sax Improvisation Blog Of Saxophonist Bobby Stern Bobbysternjazz Com



3 1 6 Musical Composition Digital Sound Music




Naming Major Or Minor Triads In Music Theory Chord Inversions




Learn 6 Ways To Play E Augmented Chord By Chord Acoustic Guitar




Basicmusictheory Com G Augmented Triad Chord




Basicmusictheory Com G Sharp Augmented Triad Chord



Jazclass Jazz Theory 12 7th Chords 2



Bass Guitar Augmented Triads Root Position Sheet Music For Bass Solo Musescore Com




Basicmusictheory Com G Sharp Augmented Triad Chord
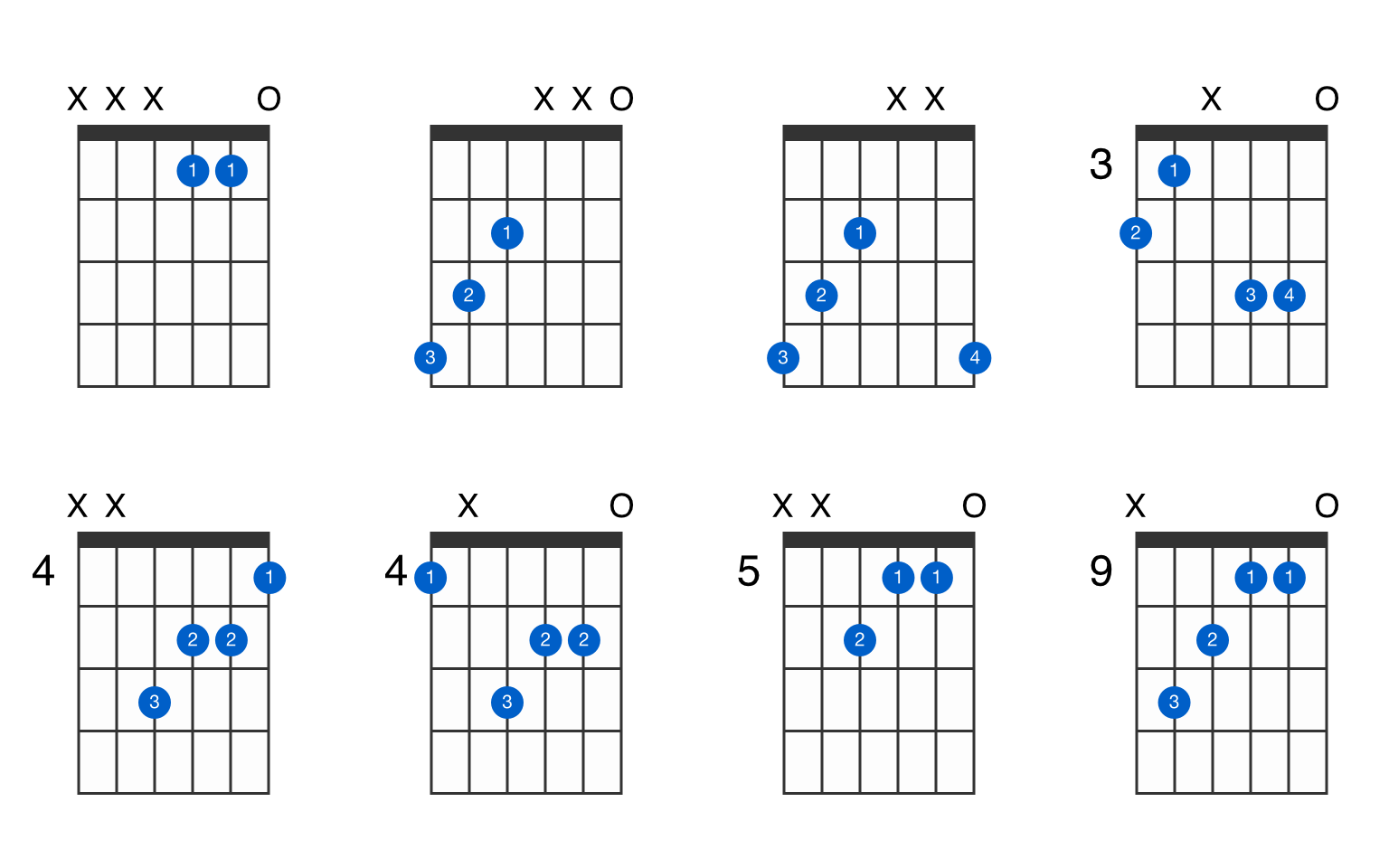



G Sharp Augmented Guitar Chord Gtrlib Chords




Guitar Triads Musical Notation Melody




5 2 Naming Triads




Basicmusictheory Com G Flat Augmented Triad Chord




Triads Music Theory Academy




Rob Silver Four String Augmented Triad Arpeggios For 7 String Guitar All String And All Inversions




5 2 Naming Triads
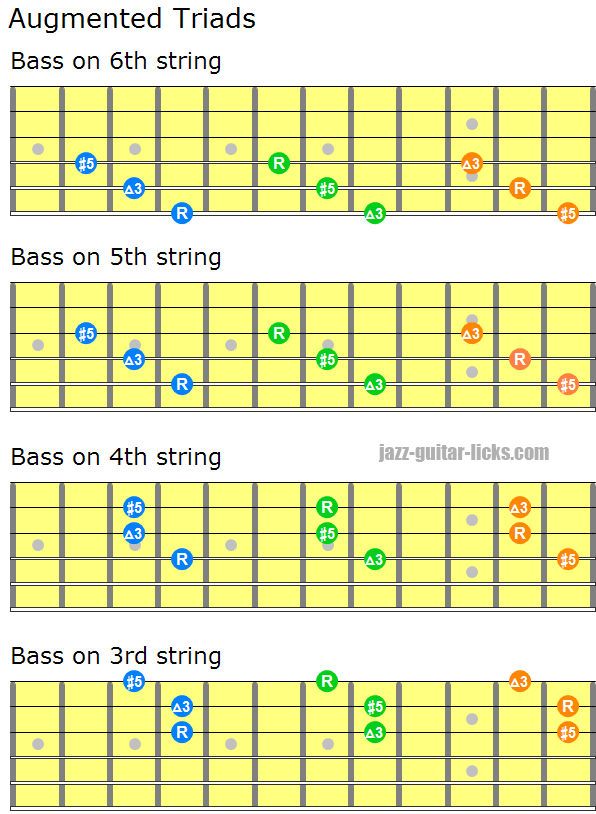



Augmented Triad Chords Guitar Diagrams And Voicing Charts




Root Position Triads Music Theory Fundamentals Lecture 10 Youtube




Basicmusictheory Com G Flat Augmented Triad Chord
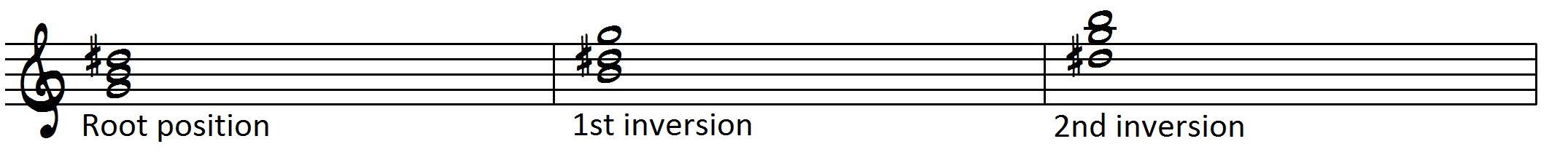



Mastering The Fretboard Augmented Triads Learn Jazz Standards
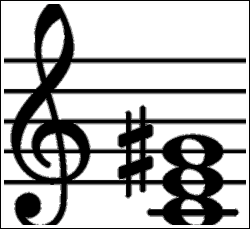



The Augmented Chord Music Theory For Mandolin Simplymandolin




Augmented Options Open Music Theory




Understanding Inversions Music Practice Theory Stack Exchange




Augmented Guitar Chords From The Augmented Scale Everyguitarchord
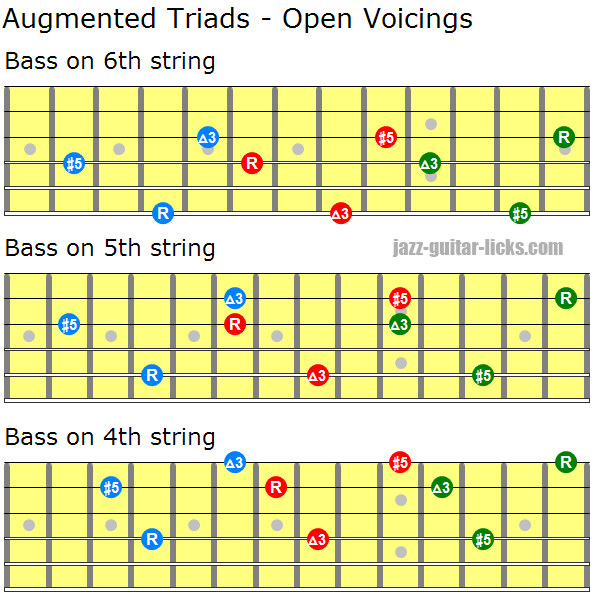



Augmented Triad Chords Guitar Diagrams And Voicing Charts
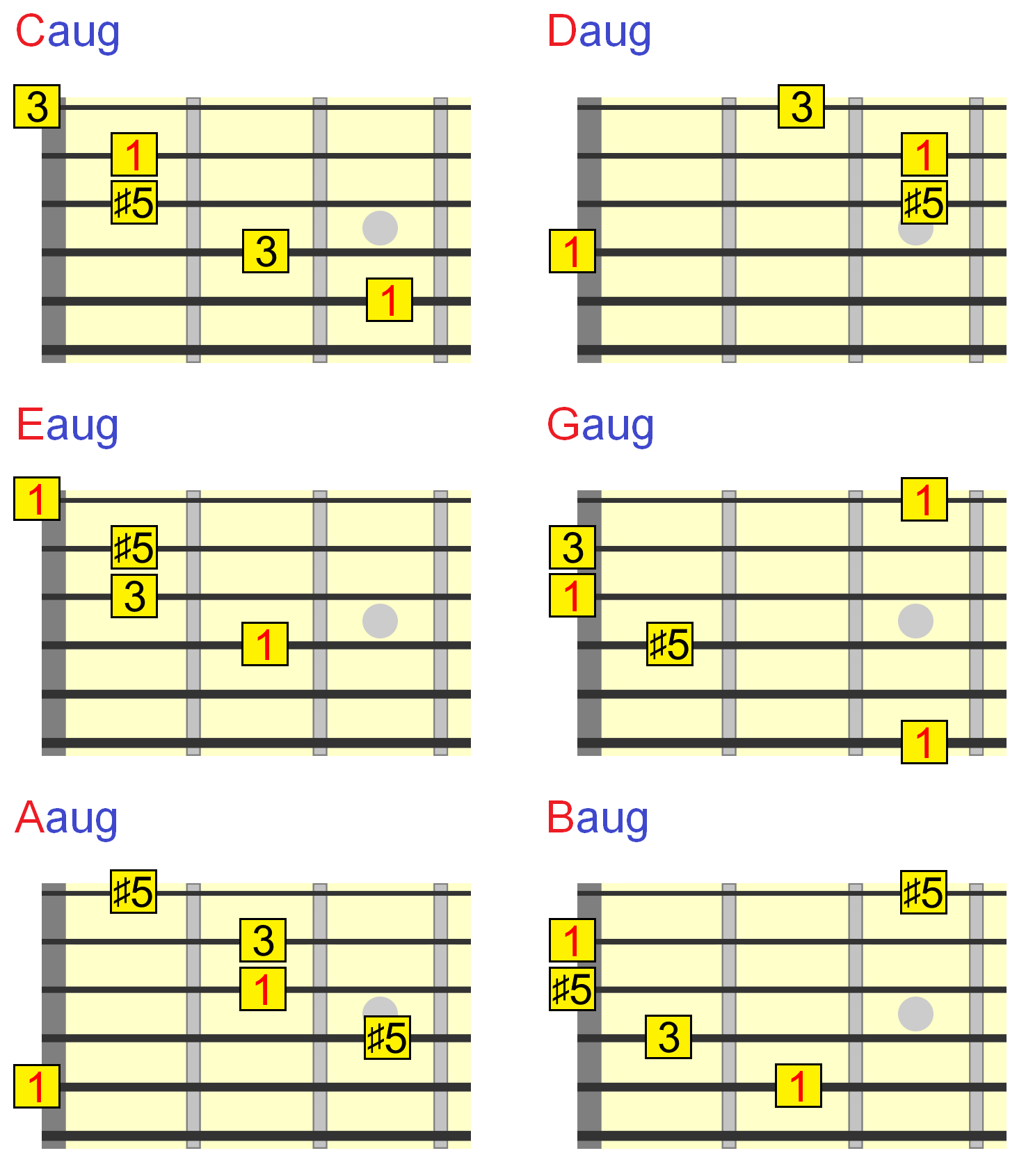



Augmented Guitar Chords Everything You Need To Know



1



1



13 Triads Fundamentals Function And Form
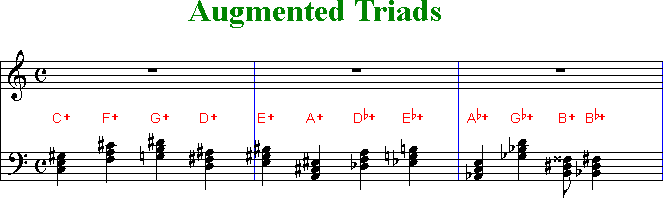



Music Secrets Of Chords
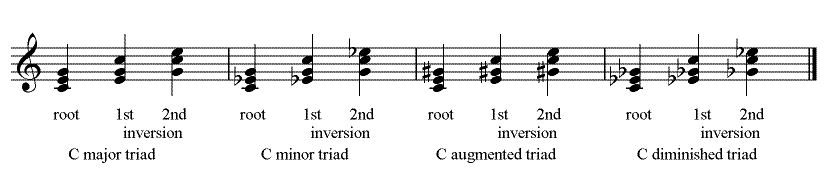



Dolmetsch Online Music Theory Online Triads Chords
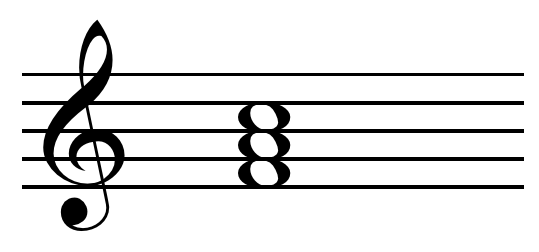



Root Position Wikipedia



Unit 13 Music 110 Fundamentals Of Theory



Augmented And Diminished Chords Open Textbooks For Hong Kong




Integrated Aural Skills Ear Training Triads In Review



13 Triads Fundamentals Function And Form




Triads The International Institute Of Bassists




Basicmusictheory Com G Major Triad Chord



Mastering The Fretboard Augmented Triads Learn Jazz Standards



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿